Checklist for Designing AI Training Modules
NWA AI Team
Editor
Checklist for Designing AI Training Modules
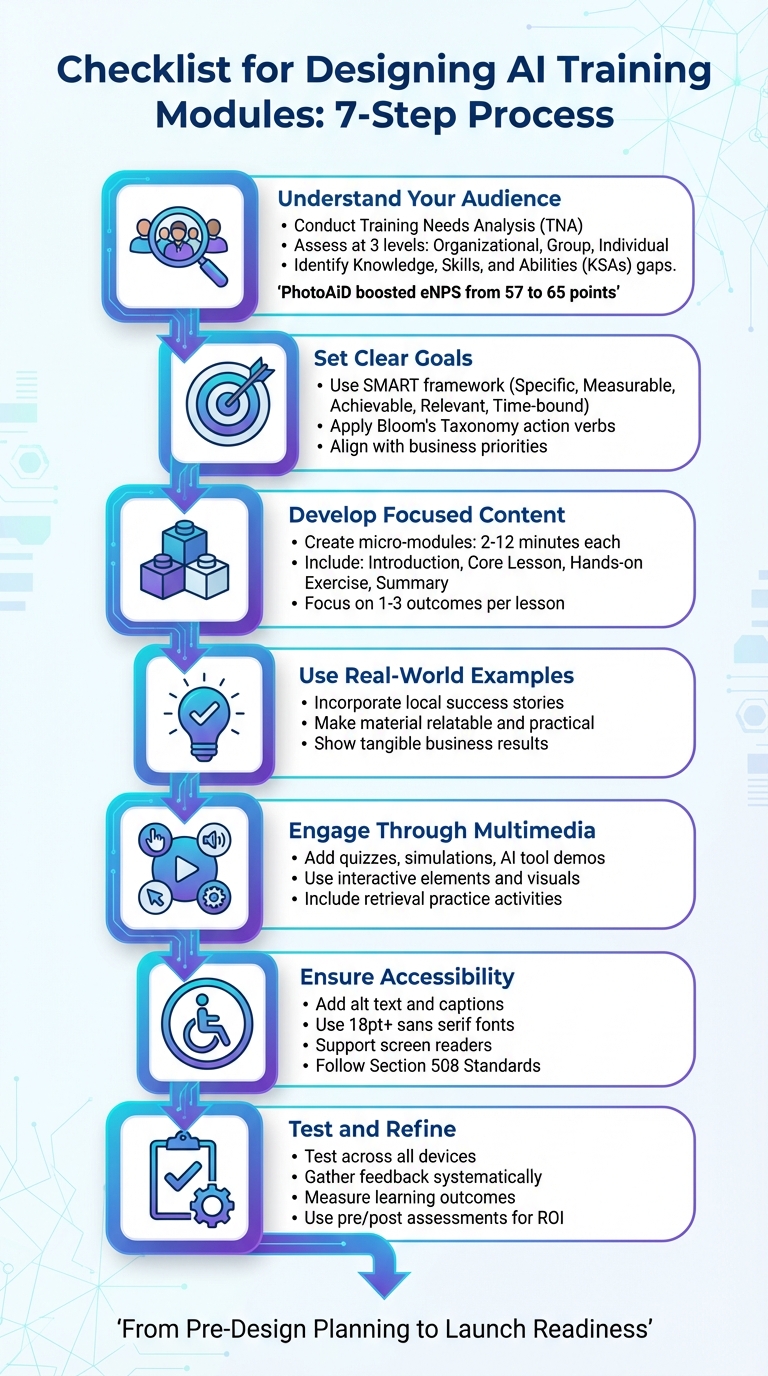
Want to create effective AI training modules? Here's how to get started. This guide covers everything you need to know about building AI-focused training programs that work. From identifying your team's skill gaps to creating hands-on exercises, we've got you covered. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Understand your audience: Conduct a Training Needs Analysis (TNA) to pinpoint knowledge gaps at organizational, group, and individual levels.
- Set clear goals: Use the SMART framework and Bloom's Taxonomy to define measurable learning objectives.
- Develop focused content: Break topics into micro-modules (2–12 minutes) with introductions, core lessons, and hands-on exercises.
- Use real-world examples: Incorporate local success stories and practical applications to make the material relatable.
- Engage through multimedia: Add interactive elements like quizzes, simulations, and AI tool demos to keep learners involved.
- Ensure accessibility: Follow best practices for usability, including alt text, captions, and screen reader compatibility.
- Test and refine: Check functionality across devices, gather feedback, and measure learning outcomes.
AI Training Module Design Checklist: 7-Step Process
Pre-Design Planning Checklist
Identify Audience Needs and Knowledge Gaps
Before creating any training material, it’s crucial to assess where your team currently stands. Conduct a Training Needs Analysis (TNA) at three levels: organizational (company-wide goals), group or job role (departmental skills), and individual (personal development needs). This ensures decisions are based on data, not assumptions.
Start by gathering information through employee surveys, performance reviews, direct observations, and interviews with department heads. Look for gaps in Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (KSAs). For example:
- Knowledge might include theoretical concepts like AI principles.
- Skills refer to practical abilities, such as Python programming.
- Abilities involve applying those skills to real-world tasks.
Take PhotoAiD as an example. In 2024, the company conducted a TNA led by Karolina Kijowska, Head of People & Culture. The analysis led to customized learning programs, which boosted their employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) from 57 to 65 points by addressing specific skill gaps.
"Training needs analysis is critical if you want to ensure you don't waste resources, time, and energy. When done correctly, people learn more quickly, there is a greater impact on job performance, and it reduces the frustration that comes for employees."
– Emily Chipman, Executive Coach and Principal Consultant, Rushman Consulting Solutions
However, not all performance issues stem from a lack of training. Sometimes the root cause lies in other areas, such as workplace culture, resource shortages, or management challenges. As Terry Traut, CEO of Entelechy, points out:
"We may find that skills and knowledge are not the issue – or not the only issue. To increase performance, perhaps a simple job aid is required; sometimes it's as simple as telling people what's required; other times perhaps employees would benefit from a mentoring or coaching program".
Once audience needs are clear, you can define focused learning objectives to guide content development.
Define Learning Objectives
After identifying your audience’s needs, the next step is setting clear, measurable goals using the SMART framework (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound). These goals should outline what participants should be able to do after training. This “backward design” approach ensures every piece of content has a purpose.
Use action verbs from Bloom's Taxonomy to craft objectives that are both observable and assessable:
- For basic knowledge, use verbs like "Identify" or "List."
- For advanced skills, choose verbs such as "Analyze," "Evaluate," or "Create" .
For instance, instead of saying, “Understand AI tools,” a more precise objective would be: “Craft effective prompts for marketing automation.”
Make sure your objectives align with business priorities. For example, if your company in Northwest Arkansas is focused on digital transformation or boosting ROI, your training should directly support those goals. Update existing materials to reflect relevant skills like identifying AI hallucinations or performing ethical risk assessments. Collaborate with stakeholders across departments to ensure the objectives address real workplace challenges.
Determine Resources and Timeline
To scope your training effectively, evaluate your organization’s AI maturity level. For example:
- Level 1 organizations may only need basic AI tools like Microsoft Copilot.
- Level 4 organizations might require expertise in advanced machine learning and robust infrastructure.
Key resources include:
- Data assets like structured datasets and domain-specific knowledge.
- Technical infrastructure such as compute power, storage, and network capacity.
- Skilled personnel like model developers and AI ethics specialists.
For professionals in Northwest Arkansas, local resources can simplify training logistics. The Northwest Technical Institute (NWTI) in Springdale offers in-person training and testing, while the NWA AI Innovation Hub provides hands-on AI programs and adoption strategies without requiring coding expertise (https://nwaai.org).
When planning timelines, consider the complexity of the project. Simpler solutions like Microsoft Copilot can be implemented in days or weeks, while custom AI workloads might take months. Add a 20–30% buffer for unexpected challenges or learning curves. A Proof of Concept (PoC) can help validate feasibility early on, minimizing risks and refining timelines.
Here’s a practical breakdown of project timelines and complexity:
| AI Solution Type | Estimated Delivery Timeline | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Copilots | Days to Weeks | Low (Level 1–2) |
| Custom Generative AI (No RAG) | Weeks | Medium (Level 2) |
| Custom AI Workloads (with RAG) | Weeks to Months | High (Level 3) |
| Large-scale ML Model Training | Months | Very High (Level 4) |
Content Development Checklist
Break Down AI Topics into Smaller Modules
Organize your content into compact, goal-oriented modules. Start by identifying clear end-goals and align your material to meet those objectives. This approach ensures focus and avoids unnecessary detours.
For AI training, aim to create micro-learning modules lasting between 2 to 12 minutes. Each module should include an introduction, core content, a hands-on exercise, and a summary. Keep the scope manageable - focus on 1–3 specific learning outcomes per lesson and 5–10 broader outcomes for an entire course. Use Bloom’s Taxonomy to guide the progression, starting with foundational knowledge (like understanding AI’s capabilities and limitations) and advancing to skills such as evaluating the accuracy of AI-generated content. A Fall 2023 MIT Sloan survey revealed that 82% of students used generative AI for coursework, with 81% relying on it at least once a week.
Define module objectives using active verbs that describe measurable actions. For instance, instead of saying "understand prompt engineering", use "create three distinct prompt types for marketing automation" or "evaluate an AI-generated report for inaccuracies". Consider adopting a flipped classroom model: assign foundational readings or videos as pre-work, reserving live sessions for collaborative problem-solving.
| Module Component | Recommended Duration | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | 2 minutes | Context and "Why it matters" |
| Core Concept Unit | 4–8 minutes | Foundational knowledge/Theory |
| Practical Application | 10–12 minutes | Hands-on creation or prompt engineering |
| Assessment | 5–10 minutes | Knowledge check and retrieval practice |
| Summary | 1 minute | Key takeaways and next steps |
With these well-structured modules, you can incorporate practical activities to solidify learning.
Include Hands-On Exercises
To help learners develop practical AI skills, complement theoretical lessons with activities that mimic real-world scenarios. For example, in a lesson on prompt engineering, try a "Card Sorting" activity where participants use physical or digital cards to combine prompt elements - like persona, objective, and context - to create tailored prompts for specific tasks. This hands-on method highlights how minor changes in wording can significantly impact AI outputs.
Encourage critical thinking with exercises like a "Sort & Check" activity, where learners classify images or text as either AI-generated or human-made, helping them recognize key markers. Follow this with a "Citation Guessing Game" where participants verify quotes and references to identify fabricated information.
For workplace scenarios, simulate tasks like workflow automation. In healthcare, AI-powered stroke triage systems have reduced door-to-needle times by nearly half, cutting the median time from 59.05 minutes to 29.78 minutes. You can replicate these concepts by having learners practice automating processes like prior-authorization paperwork, which can lower costs from $3.41 to just $0.05 per transaction. Additionally, tools like Microsoft Dragon Medical One have helped 92% of users improve efficiency, with two-thirds reporting reduced burnout from automated note creation.
Introduce tiered activities to match varying skill levels. Beginners can refine simple prompts, while advanced learners tackle multi-step workflows. Peer review sessions can also be valuable, allowing learners to critique AI-generated outputs in small groups. For governance training, have participants draft workplace AI policies to explore the implications of oversight.
Tailor these exercises with examples from local businesses to make the content more relatable and actionable.
Use Examples from Local Businesses
Using local success stories demonstrates how AI tools are solving problems in familiar settings, making the training more relevant and relatable. For example, in 2023, University of Arkansas researcher Pantha developed an LSTM model to predict surgical supply demand for Fayetteville-based centers. By applying a Two-Stage Stochastic Programming approach, the model outperformed traditional methods and achieved a financial gain of $2,328.304. This example shows how combining demand forecasting with inventory optimization can reduce waste in healthcare.
Fayetteville health systems have also adopted AI tools like Pulsara and Viz.ai to automate stroke detection. According to an American Heart Association study, these tools reduced door-to-CT times by about 43% and door-to-needle times by nearly 49.5%. As noted in the study:
The automated LVO alert arrives within minutes of CTA completion, far earlier than human interpretation, and in many cases even before the CTA images were available for review.
However, regional challenges like slow Wi-Fi in rural areas and technology literacy gaps can hinder access to digital health services. Jennifer Andersen from the UAMS Institute for Community Health Innovation highlighted:
To reach underserved populations, we must recognize the barriers they may face when accessing digital health services so we can create solutions and reach the people who may not have the means to go to their doctor appointments regularly.
For businesses in Northwest Arkansas seeking practical AI training, NWA AI offers programs like AI Leverage, which focuses on real-world applications without requiring coding expertise. These programs help teams master tools and build workflows that deliver measurable productivity gains - an approach that bridges the gap between theory and practice. Learn more at NWA AI.
Interactive and Multimedia Design Checklist
Add Visual and Interactive Elements
Once you've built solid content modules, it's time to focus on engaging learners with interactive and multimedia elements. Static content tends to lose attention quickly, so incorporating tools like simulations, case studies, and interactive problem sets can shift learners from simply observing to actively applying what they've learned. Activities like analyzing AI outputs or crafting prompt strategies encourage deeper involvement in higher-order tasks.
When using visuals, keep them clean, relevant, and directly tied to the topic. This helps clarify concepts without overwhelming learners. Navigation should be intuitive - include clear elements like numbered pages, a contents menu, and Home and Exit buttons to guide learners seamlessly through the material.
For AI training, consider starting each session with retrieval practice, such as low-stakes quizzes. These not only encourage learners to complete pre-work but also help reinforce their ability to recall information. AI chatbots can also be integrated as interactive tools, providing real-time exploration of topics like prompt engineering. Assessments should reflect real-world scenarios aligned with your learning objectives, offering meaningful feedback to strengthen newly acquired skills.
| Bloom's Taxonomy Level | Interactive Assessment Examples |
|---|---|
| Create | Research projects, business plans, website designs |
| Evaluate | Product reviews, critiques, journals |
| Analyze | Case studies, debates, concept maps |
| Apply | Simulations, labs, problem sets |
Ensure Accessibility and Usability
Delivering content in multiple formats - audio, visual, and text - ensures it meets the needs of various learning styles and abilities. Every image or GIF should include alt text and avoid relying solely on color to convey meaning.
Be mindful of animations. Avoid flashing, strobing, or parallax effects, as these can trigger seizures or vertigo. Similarly, steer clear of striped or checkered patterns and saturated reds, which may pose health risks for individuals with epilepsy or traumatic brain injuries.
For accessibility, use unique titles on every slide or page to help screen reader users, and organize headings in a logical, nested structure (e.g., Heading 1 followed by Heading 2). Videos should include human-transcribed captions and HTML transcripts. Presenters should describe on-screen visuals for those relying on audio accessibility. Stick to sans serif fonts at 18pt or larger, ensure ample white space, and include slide numbers for live sessions. Avoid placing critical information in headers or footers, as assistive technology might skip over these areas.
"Content should be conveyed in multiple ways - audio, visual, and text - to account for different learning modes." – UMass Office of the President
Be clear about when AI is required, allowed, or restricted in assessments. For example, banning AI tools in in-person evaluations could disadvantage students with disabilities who rely on them for writing. Always state system requirements upfront.
These accessibility practices lay the foundation for the interactive demos discussed in the next section.
Include No-Code AI Tool Demonstrations
After ensuring your content is both accessible and interactive, take it a step further by integrating hands-on demos of AI tools. Static screenshots can't compare to the immersive experience of interactive demos. Platforms like Supademo and Guideflow let you create "sandbox" environments and step-by-step guides without needing any coding skills. These tools even use AI to auto-generate text descriptions, synthetic voiceovers, and translations in over 15 languages.
The impact of interactive demos is clear. For instance, VRIFY cut their enablement content production time by 75% and saved over $100,000 in staffing costs. Similarly, Bullhorn saw a 20% boost in viewer engagement and produced training materials 50% faster. Meanwhile, Captain Data doubled customer ticket resolution efficiency and reduced support tickets by 20%.
Embed these demos directly into your LMS platform, website, or knowledge base, enabling learners to engage at their own pace. Use trackable links to monitor engagement and completion rates. Prioritize sandbox environments that mimic real-world product experiences, allowing learners to explore safely.
In Northwest Arkansas, NWA AI offers hands-on AI Leverage courses designed to teach practical tool usage and workflow creation - no coding required. These interactive, no-code programs empower teams to achieve measurable productivity improvements. For more details, visit NWA AI.
sbb-itb-e5dd83f
Technical and Launch Readiness Checklist
Select the Right LMS Platform
Wrapping up your AI training design means ensuring everything is ready for launch, from technical checks to feedback systems. A solid Learning Management System (LMS) is at the heart of this process. It should track progress effectively and integrate with AI tools without a hitch. Many modern LMS platforms now include AI-powered personalized learning and mobile access, making them a great fit for today's learners. For smaller teams, lightweight platforms with gamification features can be a budget-friendly option. If you're training both internal staff and external partners, look for an LMS with multi-tenant capabilities to manage different groups from a single platform.
Technical compatibility is a must. Your LMS should support SCORM (1.2 and 2004) and xAPI (Tin Can API) standards to ensure smooth communication between training modules and the system, tracking both online and offline learner activities. Single Sign-On (SSO) integration is another key feature, as it allows users to log in using existing credentials from HRMS or ERP systems, reducing barriers to access. Offline functionality is also critical - learners should be able to download materials and access them without an internet connection, especially for mobile-first users.
After selecting your LMS, thoroughly test its compatibility and performance on all devices to avoid surprises during launch.
Test for Functionality and Compatibility
Before rolling out your training, make sure it works seamlessly across all devices - whether it's an Android phone, iPhone, iPad, laptop, or desktop PC. Responsive layouts should adapt to different screen sizes without compromising usability. A pre-launch quality assurance (QA) evaluation should cover these essentials:
- Navigation elements like Home and Exit buttons, page numbering, and menus should work consistently.
- Interactive features such as quizzes, simulations, and assessments must record data accurately within the LMS.
- External links to resources and glossaries should be functional and up to date.
- System requirements should be clearly stated at the beginning of the module.
Additionally, ensure the training meets Section 508 Standards, so navigation and interactive elements are accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities.
Once the modules pass these tests, focus on setting up a system to gather and analyze user feedback.
Prepare Feedback and Evaluation Systems
A robust feedback system is essential for tracking the success of your training. Start by defining your metrics - whether you're measuring usability, engagement, or learning outcomes - and pick the right tools for the job. Use pre-assessments to establish a baseline and post-assessments to measure ROI. Your LMS should include an analytics dashboard to monitor progress and performance in real time.
In-app surveys are a great way to gather feedback without pulling users out of the training environment, which often leads to higher response rates. Segment your audience to tailor questions for those who’ve completed specific modules, and automate follow-ups to collect reviews immediately after key milestones. Encourage honest course ratings and reviews to pinpoint gaps and identify outdated content. For AI-focused training, evaluate whether learners can identify incorrect AI outputs and whether they’ve gained enough expertise to critique AI-generated results effectively.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Creating effective AI training modules is all about delivering a learning experience that sticks. The foundation for success lies in identifying your audience's knowledge gaps and setting clear, measurable goals before diving into content creation. The best training programs incorporate hands-on exercises and real-world scenarios, which not only make the material engaging but also encourage adoption. As Gaby Lio, an AI Innovation Expert at CGI, puts it:
AI literacy is more than just trainings... It includes hands-on practice, good judgment, and knowing when to trust, challenge or complement AI output.
To ensure your training hits the mark, both technical readiness and quality content are key. Your modules should meet accessibility standards, work seamlessly across devices, and include secure environments where learners can safely experiment. The impact of effective training is clear: faster project turnarounds, boosted productivity, and happier employees. For example, in August 2025, Newark government planners piloted an AI tool that transformed 90-minute council meetings into concise two-minute action lists, showing how well-designed AI training can save time and improve efficiency.
These takeaways provide a solid foundation for putting AI training into action.
Next Steps
Armed with these insights, it's time to take the first step. Begin with a pilot project - perhaps using AI to summarize lengthy meetings or automate repetitive tasks. Test your training modules before a full rollout, and set up feedback loops to refine and improve as you go.
For those in Northwest Arkansas looking for expert guidance, NWA AI offers hands-on training tailored to your team's workflows. Their programs focus on practical applications of AI tools, no coding required, helping teams reimagine their processes. Visit https://nwaai.org to learn more about their training options and start advancing your AI literacy today.
How can I use AI to aid my training design? (10 ways AI can help training design)
FAQs
How can I identify AI skill gaps within my organization?
To pinpoint where your organization might be lacking in AI expertise, start with a skills-gap analysis. This means comparing the AI skills your team needs to meet your business objectives with the skills they currently have. Identify the essential abilities for each role - such as prompt engineering, AI ethics, and knowledge of specific tools like Microsoft Copilot or Azure AI services. Use tools like self-assessment surveys, manager feedback, and hands-on tasks to evaluate your team's current proficiency.
Compile this data into a skills matrix to clearly see where the gaps are. Then, prioritize these areas based on how much they impact your business goals and turn them into actionable learning objectives. From there, you can create a targeted training plan to address these gaps effectively.
For training solutions, consider NWA AI's hands-on workshops, which include sessions on prompt design and AI ethics. These programs are tailored to help your team build skills quickly - even if they don’t have a technical background - so you can bridge critical gaps and encourage broader AI adoption within your organization.
How can hands-on exercises make AI training more effective?
Hands-on exercises are a fantastic way to transform abstract AI concepts into practical, usable skills. By directly experimenting with AI tools, learners can bridge the gap between theory and application. For instance, short, interactive sessions where participants design and test prompts using live AI tools not only build confidence but also reinforce core ideas. Adding guided worksheets with clear, step-by-step instructions and examples can make these exercises even more approachable, helping learners reflect on what they’ve learned.
Creating a sandbox environment - a safe and controlled space where learners can practice, receive immediate feedback, and refine their approach without worrying about mistakes - further strengthens their understanding. Collaborative activities, like tackling real-world challenges in small groups, add another layer of engagement. They encourage teamwork, spark discussions, and prompt learners to think critically about the ethical considerations surrounding AI.
At NWA AI, we’ve embraced these methods in our training programs. By offering structured labs, dedicated practice environments, and group projects, we empower professionals to develop AI skills quickly and responsibly - no coding expertise required.
What steps can I take to make AI training modules accessible to everyone?
To ensure AI training modules are accessible to everyone, focus on universal design principles and follow established accessibility standards. Start by incorporating features like captions or transcripts for videos, alt text for images, and making sure all interactive elements work seamlessly with keyboards and screen readers. Providing content in various formats - such as text, audio, and visuals - gives learners more flexibility. Additionally, include options for adjusting font size, contrast, and playback speed to accommodate individual needs.
It's also important to test your modules with a diverse group of learners, including those who rely on assistive technologies. Use their feedback to make meaningful improvements. Keep instructions straightforward, divide content into smaller, digestible sections, and offer optional resources for those who may need extra support. By taking these steps, you create training modules that are inclusive and effective, reflecting NWA AI's commitment to making AI education accessible to the entire Northwest Arkansas community.
Ready to Transform Your Business with AI?
Join our AI training programs and help Northwest Arkansas lead in the AI revolution.
Get Started TodayRelated Articles

ROI and KPIs in AI Process Optimization
Measure AI impact with ROI and KPIs: set baselines, track hard and soft ROI, and monitor model, system, and business KPIs to validate performance and value.

How Blended Learning Improves AI Upskilling
Blended learning—online modules plus hands-on workshops—boosts AI skill retention, engagement, and real-world application for faster workplace upskilling.

5 Steps to Define AI Workflow Goals
Set measurable AI workflow goals in five steps: map processes, set SMART targets, pinpoint AI opportunities, define KPIs, and align with strategy.
