AI Training vs. Traditional Upskilling: Key Differences
NWA AI Team
Editor

AI Training vs. Traditional Upskilling: Key Differences
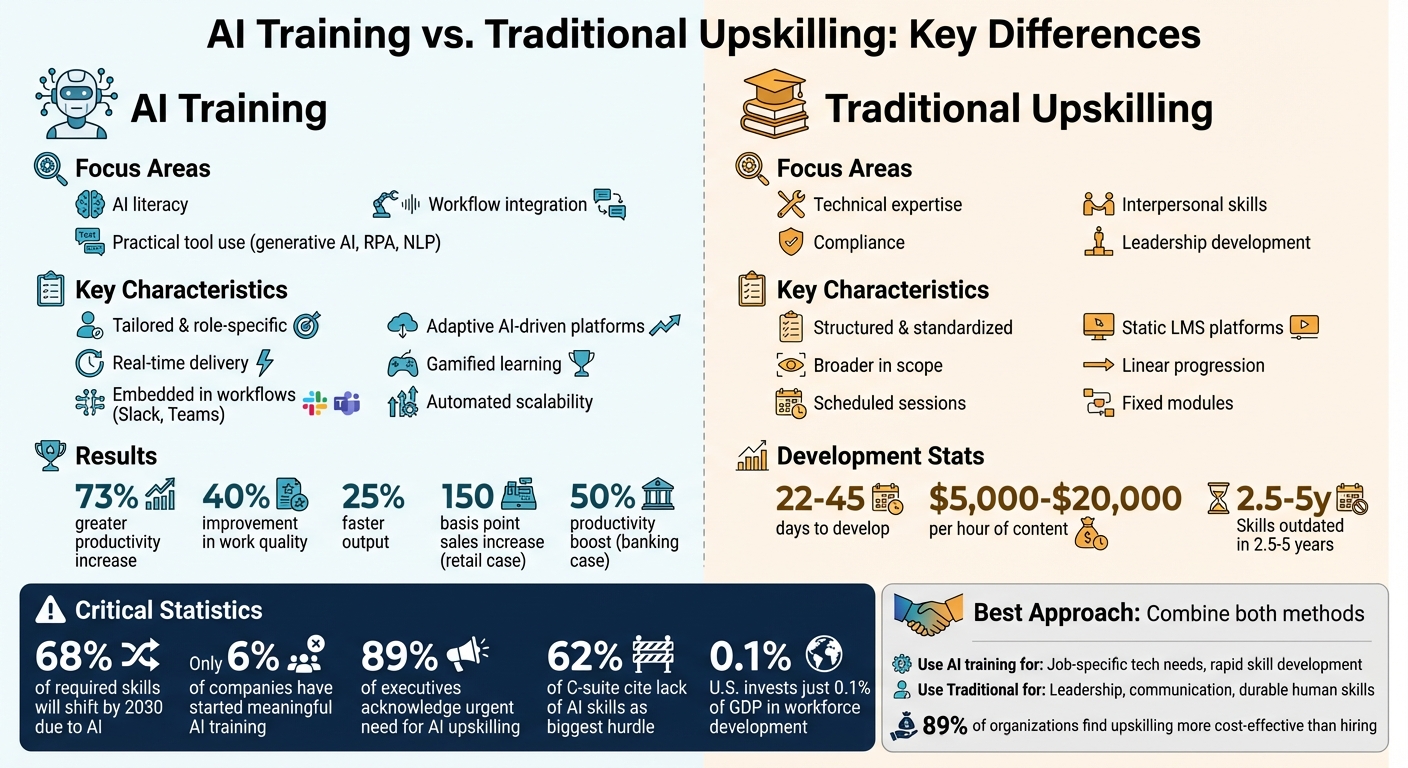
AI training and traditional upskilling differ in both approach and outcomes. AI training focuses on equipping workers with skills to use AI tools effectively, such as generative AI and machine learning, through personalized, real-time learning integrated into daily tasks. Traditional upskilling emphasizes refining existing skills, like leadership or technical expertise, through structured, standardized programs.
Key takeaways:
- AI Training: Tailored, role-specific, and delivered in real-time; focuses on AI literacy, tool usage, and workflow integration.
- Traditional Upskilling: Structured, broader in scope; focuses on interpersonal and durable skills that remain relevant over time.
Quick stats:
- By 2030, 68% of required skills will shift due to AI.
- Only 6% of companies have started meaningful AI training programs.
- U.S. invests just 0.1% of GDP in workforce development, lagging behind other nations.
Choosing the right approach depends on your goals. Use AI training for job-specific technological needs, and traditional methods for skills like communication or leadership. A combined approach ensures better results by addressing both immediate and long-term workforce needs.
AI Training vs Traditional Upskilling: Key Differences and Features Comparison
Main Features of AI Training and Traditional Upskilling
AI Training: Preparing for AI-Driven Work
AI training programs focus on three main areas to help employees work effectively alongside AI: AI literacy, practical tool use, and workflow integration. AI literacy provides employees with the foundational knowledge they need to grasp what AI can do and its limitations. It’s not about learning to code but about understanding how AI can be applied and the potential risks it carries.
The second focus is on practical tool use. Participants get hands-on experience with technologies like generative AI, robotic process automation, and natural language processing. This includes learning skills like prompt engineering to make these tools work effectively. Lastly, workflow integration ensures that AI becomes part of daily operations, helping to streamline tasks and manage complex, multi-step processes.
Some companies, like IBM, organize their training into tiers - AI Awareness, AI Builders, and AI Masters - aligning the training to employees’ skill levels. The overarching goal is to use AI as a tool to enhance human productivity, not to replace it.
Traditional Upskilling: Developing Core Skills
Traditional upskilling takes a broader approach, focusing on areas like technical expertise, compliance, interpersonal skills, and leadership. These programs are designed to prepare employees for both their current roles and long-term career growth. They often follow a fixed, linear structure, where participants move through pre-set modules at a steady pace, whether in group sessions or self-paced online formats.
Developing these traditional training modules can take anywhere from 22 to 45 days, with costs ranging from $5,000 to $20,000 per hour of content. These programs aim to build long-lasting, foundational skills. However, this contrasts with the fast-changing nature of AI, where skills and tools can become outdated in just 2.5 to 5 years.
AI training for Employees: Essential Guide for Upskilling and Reskilling
How AI Training and Traditional Upskilling Differ
Understanding the differences between AI training and traditional upskilling is key to reshaping workforce development strategies in today’s fast-paced environment.
Design and Customization
Traditional upskilling often takes a standardized approach, teaching foundational concepts but rarely connecting them to employees' day-to-day tasks. These programs can feel static, leaving employees with knowledge that isn’t always actionable. On the other hand, AI training is built around specific roles - like Shapers, Leaders, Transformers, and Frontline Contributors - making it highly relevant to actual work scenarios. This method ensures a progression from learning the basics to applying new skills on the job, with the ultimate goal of integrating these skills into daily routines.
Kaye Foster, former CHRO at Johnson & Johnson, highlighted this gap in traditional methods:
We assume that if leaders know what to do, they'll do it. That's just not true. Most of the time, leaders revert to the behaviors that are reinforced, not the ones they learn in training.
AI training focuses on high-impact areas where it can deliver significant returns. For example, a European retail bank revamped its lending operations by introducing an "Ops AI Agent." This redesign cut loan approval times from several days to under 30 minutes, boosting productivity by 50%. Unlike the rigid structure of traditional programs, this targeted approach aligns training with tangible business outcomes.
Technology and Platforms
The technology supporting AI training is dramatically different from that used in traditional upskilling. Traditional methods often rely on scheduled sessions through Learning Management Systems (LMS), many of which are inconveniently timed and fail to engage employees. In contrast, AI training integrates seamlessly into daily workflows, delivering real-time micro-lessons through platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams. Features like newsfeed-style updates and gamification make the learning experience more engaging and effective.
| Feature | Traditional Upskilling | AI Training |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery | Scheduled, off-hour sessions | Real-time, embedded in workflows |
| Technology | Static LMS | Adaptive, AI-driven platforms |
| Scalability | Expensive, slow customization | Automated, scalable personalization |
| Engagement | Often disconnected | Gamified, integrated learning |
A great example of this difference is Salesforce's "Career Connect" platform. Launched in Q1 2025, this AI-powered tool used machine learning to recommend personalized learning paths and match employees to internal roles. The result? Half of the company’s open positions were filled by existing staff. These advancements not only make learning more efficient but also directly improve workforce performance.
Effects on Workforce Performance and Change
The results of AI training speak for themselves. Workers paired with AI tools saw a 73% greater increase in productivity compared to those without such support. Companies incorporating AI training also reported a 40% improvement in work quality and a 25% faster output. In contrast, traditional upskilling tends to produce incremental progress rather than transformative changes.
One global retailer with over 500 locations conducted A/B testing to measure the impact of AI-focused training. The results were striking: the group receiving AI training experienced a 150 basis point increase in sales and doubled employee engagement compared to the control group. These metrics underscore the effectiveness of AI-driven methods in delivering measurable business benefits.
With technical skills becoming outdated in less than five years, timely and contextual training is critical. As Jim Link, CHRO at SHRM, explains:
When training isn't timely or contextual, both business progress and employee growth stall.
AI training’s continuous, real-time model tackles this challenge head-on, adapting to rapid technological changes. Meanwhile, traditional programs often struggle to keep pace, even as 89% of executives acknowledge the urgent need to improve their workforce’s AI skills.
sbb-itb-e5dd83f
Choosing the Right Training Approach for Your Organization
Understanding the differences between training methods can help organizations decide which approach best fits their specific needs.
When AI Training Makes Sense
AI training shines in roles where technology drives measurable outcomes. Think about positions where automation, data analysis, or AI tools directly affect business results - like customer service reps using chatbots, marketing teams creating content with generative AI, or analysts building predictive models.
The stats underline this need: 62% of C-suite executives identify a lack of AI skills as the biggest hurdle to scaling AI initiatives. Instead of trying to train everyone at once, focus on roles that are adopting AI quickly. For example, by spring 2025, nearly 47% of workers reported using AI tools monthly, a jump from 34% the previous year.
To make this work, consider role-based archetypes that reflect how employees engage with AI. Frontline Contributors, who use AI tools daily, need practical, hands-on training. On the other hand, Transformers - team leaders reshaping workflows - require both technical expertise and change management skills. A global biopharmaceutical company applied this strategy, segmenting over 100,000 employees into archetypes and tailoring their training programs. The result? AI tool adoption skyrocketed from 20% to nearly 90%.
When Traditional Upskilling Works Best
For durable skills - the kind that stay relevant no matter how technology evolves - traditional upskilling remains the gold standard. Leadership development, strategic decision-making, interpersonal communication, and safety training all benefit from conventional methods. While technical AI skills might become outdated in just a few years, human-focused skills like empathy, trust, and relationship management are timeless.
Building trust is especially critical. Brad Strock, Executive Coach and former CIO at PayPal, puts it plainly:
The real challenge with AI isn't the technology - it's getting people to trust it. If you don't build trust first, no AI initiative will succeed.
Traditional training is uniquely equipped to address these emotional and interpersonal challenges. Managers need coaching to guide teams through fears of job displacement. Executives benefit from leadership development programs to create clear, reassuring narratives about AI's role in the organization. These human-to-human skills can’t be effectively taught through AI-driven platforms alone.
Combining Both Training Methods
The best workforce transformation strategies combine AI training with traditional upskilling, meeting diverse needs at the same time. A three-part learning progression works well here:
- Foundational: Teach core concepts with online modules.
- Applied: Offer hands-on practice through labs and real-world projects.
- Embedded: Reinforce habits with mentorship and performance tracking.
This blended approach uses AI tools for personalization and skill-gap analysis while relying on traditional mentorship for guidance and support.
For organizations in Northwest Arkansas, NWA AI (https://nwaai.org) offers programs that mix AI training with traditional development. Their curriculum progresses from AI Literacy (basic concepts and strategy) to AI Leverage (practical tool training) and AI Adoption (change management and ROI measurement).
The key is to avoid the "watering can" approach - spreading resources too thinly across undifferentiated programs. Instead, start with a skills gap assessment to determine which roles need technical AI training and which require traditional development. With 89% of organizations agreeing that upskilling current employees is more cost-effective than hiring new talent, this combined strategy offers both immediate and long-term value. It equips organizations to implement AI effectively while building a resilient workforce for the future.
Conclusion
Transforming a workforce effectively means aligning training methods with the specific needs of each role. AI-focused training shines when the goal is rapid, job-specific skill development that can lead to tangible business improvements like increased productivity and faster decision-making. On the other hand, traditional upskilling remains critical for nurturing enduring human abilities such as leadership, communication, and trust-building - skills that retain their importance even as technology evolves. The impact of these distinct training approaches is evident in measurable outcomes like improved efficiency and workflow enhancements.
Interestingly, while 89% of business leaders acknowledge the growing need for advanced AI capabilities, only 6% have initiated meaningful upskilling programs to address this gap. Strategic action in this area can result in up to a 40% improvement in output quality and a 25% acceleration in achieving results.
To succeed, organizations must identify skill gaps, determine which roles require technical AI training versus traditional development, and avoid a one-size-fits-all training model. Prioritize high-impact areas - like customer service, operations, and marketing - where targeted training can deliver quick results while also reinforcing essential human skills.
Key Points to Remember
The most effective workforce transformation strategies blend AI training with traditional upskilling. Use AI training to build technical expertise and real-time adaptability, and rely on traditional methods to develop leadership, manage change, and create an environment where employees feel safe embracing new technologies. This combination not only drives immediate operational improvements but also fosters long-term adaptability - a recurring theme throughout this discussion.
For businesses in Northwest Arkansas, NWA AI (https://nwaai.org) provides a practical solution by offering programs that range from basic AI literacy to hands-on tool training and comprehensive adoption strategies. Their approach integrates technical skill development with change management, enabling companies to implement AI effectively while building a resilient workforce. With 89% of organizations agreeing that upskilling current employees is more cost-effective than hiring externally, investing in a balanced training strategy delivers immediate productivity boosts and positions businesses for sustained success. Together, these insights lay the foundation for a forward-thinking, adaptable approach to workforce training.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of incorporating AI training into daily work routines?
Integrating AI training into daily workflows offers employees the chance to learn and apply new skills as they go, making the process both practical and immediately useful. By using AI tools directly on the job, workers can develop their abilities faster, cutting out the lag between training and real-world application.
This method doesn’t just boost skills - it also enhances productivity. AI can take over repetitive tasks, giving employees more time to focus on strategic or creative projects. Teams can make quicker, data-driven decisions while AI tackles complex, time-consuming processes in the background. Plus, embedding AI knowledge into the workplace helps organizations stay ahead by encouraging innovation and drawing in top-tier talent.
On top of that, AI training helps employees feel more confident in using the technology. When people are equipped to use AI effectively and responsibly, resistance to change decreases, and a culture of growth and adaptability thrives.
How can organizations choose between AI training and traditional upskilling for their workforce?
To choose between AI-focused training and traditional upskilling, organizations need to carefully assess the unique demands of each role. This includes evaluating the skills required, how employees prefer to learn, and how well they can adapt to AI-driven changes.
For roles like managers, analysts, or product owners, AI literacy programs can be a great fit. These programs focus on understanding AI tools, addressing ethical concerns, and learning how to interpret AI outputs. They’re particularly useful for encouraging quick adaptation and driving innovation.
On the other hand, roles that demand specialized expertise - like compliance officers or skilled trades - might benefit more from traditional upskilling. These programs typically involve structured, instructor-led sessions that help employees develop stable, long-term skills.
The best approach often combines elements of both. By considering a role’s objectives, employee readiness, and the potential return on investment, organizations can create tailored training strategies. AI-focused training is great for fast skill-building and high engagement, while traditional methods might be a better fit for larger teams with similar, consistent needs. Striking the right balance ensures the workforce is well-prepared for future challenges.
Why is it important to combine AI training with traditional upskilling methods?
Combining AI training with more conventional upskilling methods is essential for building a workforce that’s ready to tackle both technological advancements and the challenges of adapting to change. While AI training focuses on developing technical expertise and foundational understanding, traditional upskilling sharpens skills like change management, specialized knowledge for specific roles, and the ability to embrace lifelong learning. Together, these approaches equip employees to use AI tools effectively in practical, everyday situations.
The pace of AI evolution means that technical skills can become outdated in just a few years. This makes it crucial to consistently update both technical abilities and broader workplace skills. By embedding AI into daily tasks through training tailored to specific roles, employees can view these tools as integral to their work rather than as separate, intimidating technologies. This strategy encourages meaningful behavior shifts, sparks creativity, and helps businesses stay ahead in a fast-changing world.
Ready to Transform Your Business with AI?
Join our AI training programs and help Northwest Arkansas lead in the AI revolution.
Get Started TodayRelated Articles

ROI and KPIs in AI Process Optimization
Measure AI impact with ROI and KPIs: set baselines, track hard and soft ROI, and monitor model, system, and business KPIs to validate performance and value.

How Blended Learning Improves AI Upskilling
Blended learning—online modules plus hands-on workshops—boosts AI skill retention, engagement, and real-world application for faster workplace upskilling.

5 Steps to Define AI Workflow Goals
Set measurable AI workflow goals in five steps: map processes, set SMART targets, pinpoint AI opportunities, define KPIs, and align with strategy.
